Alife Virtual World Blender Create Your World
In this expansive metaverse, players can live out their wildest dreams, from building empires to exploring distant locations. Welcome to the fascinating world of 3D creation! Whether you're an aspiring artist, a hobbyist, or someone interested in the digital arts, Blender 3D offers a versatile platform to bring your imaginative concepts to life. Blender is a powerful, open-source 3D creation suite that supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline—modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing, and motion tracking, even video editing, and game creation. This beginner's guide aims to introduce you to the basics of Blender and how you can start your journey into 3D creation.
Getting Started with Blender 3D
First things first, Blender is completely free to download and use, making it accessible to everyone. For good results please use our applications tried by many users which can be downloaded here:
CLICK TO DOWNLOAD
Upon opening Blender, you'll be greeted with its default screen, which might seem daunting at first. But fear not, let's break it down together.
Exploring the Interface
Blender's interface is highly customizable and consists of several editors (like the 3D viewport, timeline, outliner, etc.) that you can arrange according to your workflow. Spend some time familiarizing yourself with the layout. The 3D viewport is where you'll spend most of your time, as it's where you'll create and manipulate your objects.
Adding Objects
You can add objects to your scene by pressing Shift+A and choosing from the mesh menu. Blender offers a wide variety of primitive shapes to start with. Try adding a cube, sphere, or cylinder to your scene.
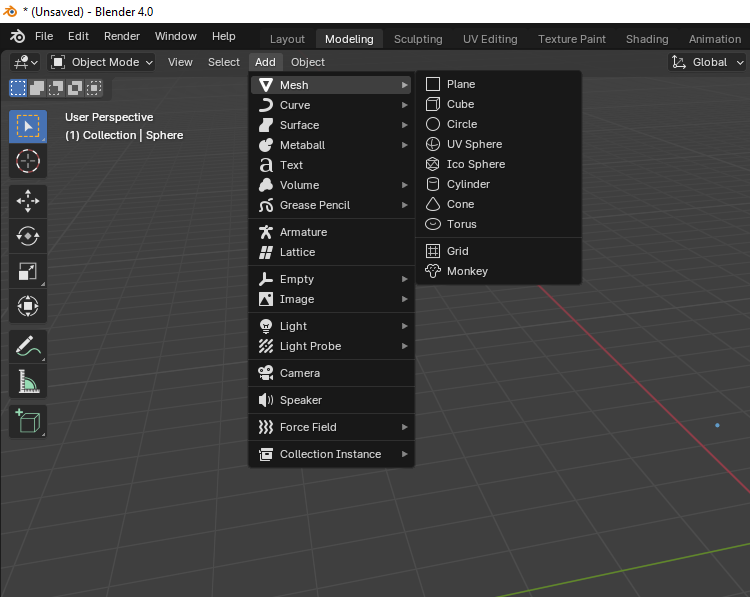
Navigation
Blender provides navigation controls to help you move around your 3D space efficiently. You can use the scroll wheel to zoom in and out. If you don't have a middle mouse button, you can customize the key map by going to Edit - Preferences - 3D View and making the necessary changes.
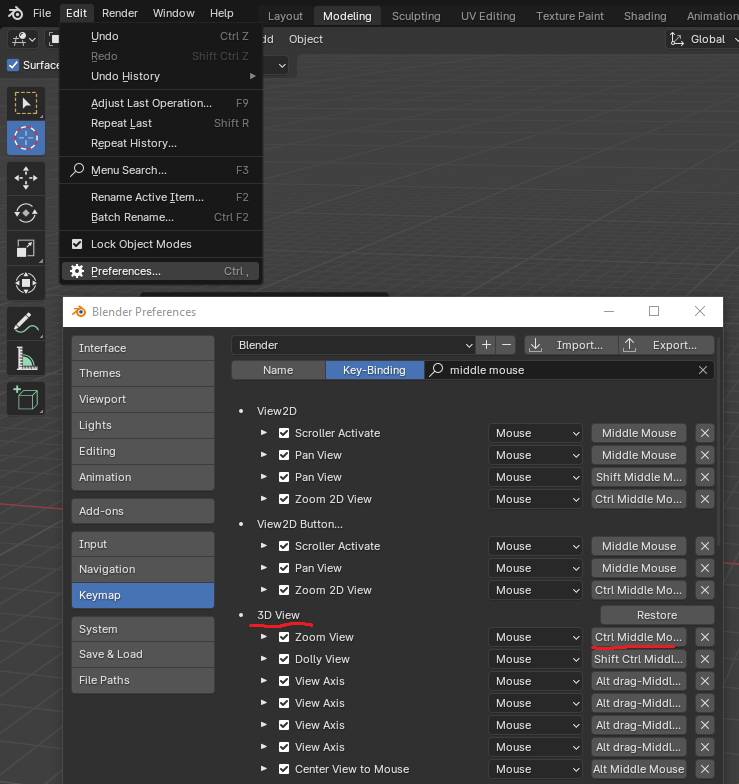
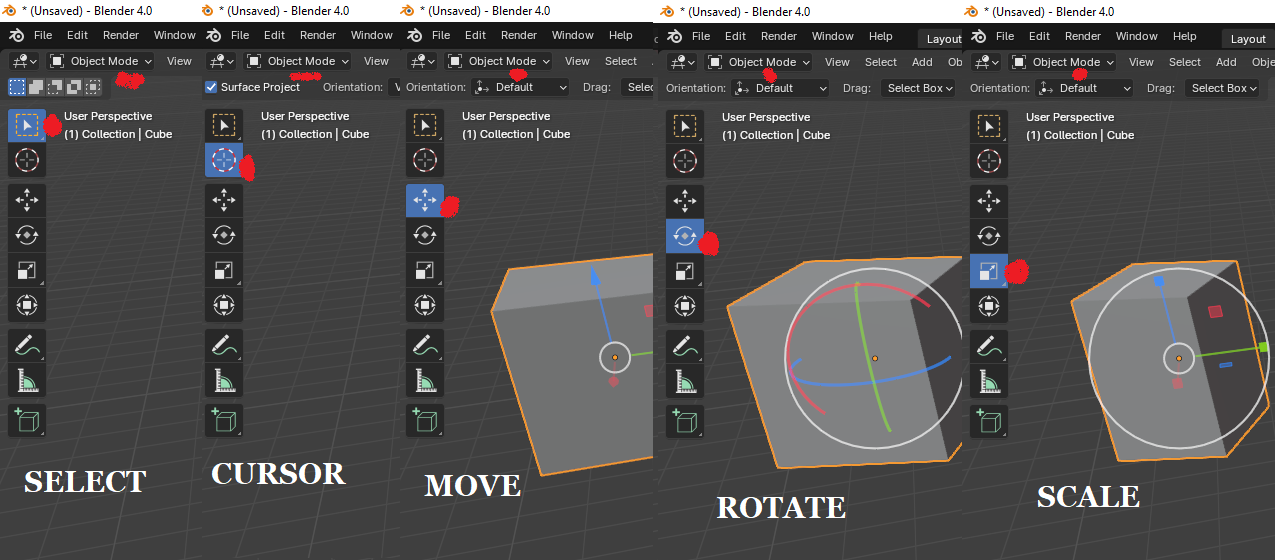
Manipulation
You can move (G), rotate (R), and scale (S) objects. Try using these commands with an object selected.
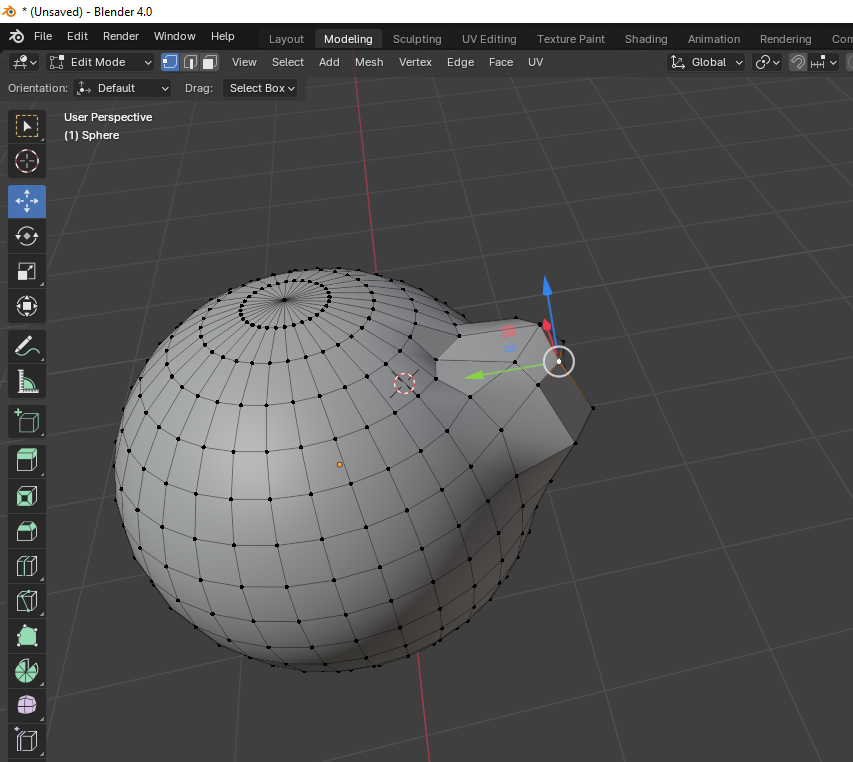
Edit Mode
You can switch between vertex, edge, and face selection modes by clicking the respective icons in the header of the 3D viewport or by using the `1`, `2`, and `3` keys on the keyboard (make sure you are not on the numpad). You can move, rotate and scale selected vertices, edges, or faces by selecting the corespoding icon in the left side of the 3D viewport and moving the mouse.
Exploring Further
Blender is incredibly deep and offers limitless possibilities. Here are a few suggestions for further exploration:
Texturing: Dive into Blender's powerful texturing tools to add realism to your models.
Lighting: Experiment with different lighting setups to enhance the mood of your scene.
Sculpting: Try Blender's sculpting tools to create more organic shapes.
Animation: Learn the basics of animation by animating your coffee cup.
Simulation: Experiment with physics simulations, like cloth or fluid simulation.
Rendering: Explore rendering engines to create stunning video of your creations.
We will provide a comprehensive tutorial with detailed explanations, accompanied by visual aids and practical examples, covering all the operations mentioned above.
Importing Files
Blender supports a wide range of file formats for importing, allowing users to work with various types of content from different sources. Here are some of the main file types supported by Blender for importing:
3D Model Files:
- .obj Wavefront
- .fbx Filmbox
- .dae Collada
- .3ds 3D Studio
- .stl Stereolithography
- .ply Stanford Polygon Library
- .x3d X3D and VRML
- .abc Alembic
- .gltf GL Transmission Format
- .svg Scalable Vector Graphics
2D Image Files:
- .jpg Joint Photographic Experts Group
- .png Portable Network Graphics
- .tif Tagged Image File Format
- .bmp Bitmap
- .hdr High Dynamic Range
- .exr OpenEXR
- .psd Adobe Photoshop
Animation Files:
- .bvh Biovision Hierarchy
- .mdd Motion Designer's Toolkit
Font Files:
- .ttf TrueType Font
- .otf OpenType Font
Audio Files:
- .wav Waveform Audio File Format
- .mp3 MPEG Layer III Audio
- .ogg Ogg Vorbis
Video Files:
- Blender can also import various video formats for video editing within its Video Sequence Editor. Supported formats can depend on the operating system and installed codecs.
Conclusion
Blender 3D is a gateway to the vast universe of 3D creation. The journey might seem overwhelming at first, but with patience and practice, you'll find it incredibly rewarding. Remember, the key to mastering Blender—or any software, for that matter—is consistent practice and exploration. Happy creating!